 Dr. Jens Hoffmann of EPO presented a webinar highlighting new data on preclinical immuno-oncology research using humanized models. The growth in immuno-oncology (IO) research has created a need for more relevant models. The IO field includes many types of drugs, including:
Dr. Jens Hoffmann of EPO presented a webinar highlighting new data on preclinical immuno-oncology research using humanized models. The growth in immuno-oncology (IO) research has created a need for more relevant models. The IO field includes many types of drugs, including: - genetically engineered immune cells such as CAR-T cells
- various antibody-based therapies such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and bi-specific T cell engagers (BITEs)
- oncolytic viruses and bacteria
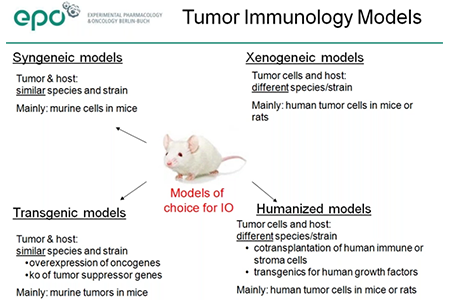
Current Options for Immuno-Oncology Models
Standard xenograft models, in which a human tumor is transplanted into an immunodeficient host, have limited utility for IO studies, as the appropriate immune cells are not present in the host. The current models of choice for IO research include:- Syngeneic models (mouse tumor transplanted into mouse of same strain background)
- Transgenic models which spontaneously develop tumors
- Humanized models (human immune and human tumor cells transplanted into an immunodeficient host)
 Learn more about preclinical immuno-oncology animal models and Read the Taconic Biosciences' Insight:
Learn more about preclinical immuno-oncology animal models and Read the Taconic Biosciences' Insight: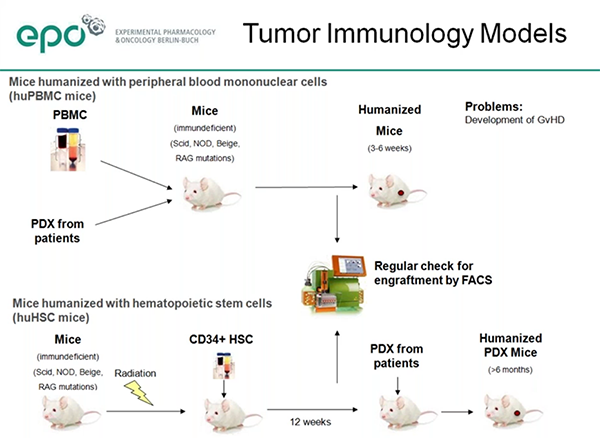
Humanized Immune System Mice in IO
Dr. Hoffmann described use of both primary types of humanized immune system mice, those engrafted with human PBMCs and those engrafted with human CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). The PBMC model (huPBMC-NOG) is well-established and quite useful, but the study window is limited as the mice eventually develop graft versus host disease. The HSC model (huNOG) takes longer to get sufficient human cell engraftment and differentiation, but has the advantage of a longer useable study window.EPO has measured stable engraftment of human immune cells up to 254 days post-engraftment in the HSC model. EPO has compared both the NOG and NOG-EXL models in the HSC engraftment model and saw, as reported by others, that overall engraftment levels were higher in the NOG-EXL. They also saw higher engraftment of T, B, NK and CD14+ monocytes in the NOG-EXL as compared to the NOG.
Preclinical Modeling of Human NK Cells
For studies requiring human NK cells, Dr. Hoffmann explained that the recently developed hIL-15 NOG mouse may be more suitable than the base NOG mouse. Following engraftment of human PBMCs, the hIL-15 NOG mice had higher engraftment of T cells compared to NOG mice, and also showed significant numbers of NK cells, which do not develop appreciably in NOG mice.The huPBMC model is appropriate for study of the many types of IO therapies, including:
- Bi-specific T cell engager antibodies (BITEs), which target a tumor antigen and recruit cytotoxic T cells
- Checkpoint inhibitors
- Oncolytic viruses
Dr. Hoffmann showed validation data demonstrating efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor therapeutics against PDX in HSC-engrafted mice. He did caution that, because of donor-to-donor variability in both tumor growth and response to immunotherapies, it is important to use multiple HSC donors in each experiment.
Preclinical Immuno-Oncology Case Study
The webinar included an interesting case study involving a head-and-neck tumor. EPO studied this tumor in several contexts: in PBMC-engrafted mice, both with three unrelated donors as well as with autologous PBMCs from the cancer patient, and with three unrelated donors in the HSC-engrafted model.In the PBMC model, the tumor grew similarly in mice humanized with the patient's autologous PBMCs and from two of the three unrelated donors, but the tumor grew much faster in the mice engrafted with one particular donor's PBMCs which happened to be well HLA-matched to the tumor.
The checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab showed good efficacy in mice from that latter donor. The head-and-neck tumor growth varied also in the HSC model across different donors, and similarly checkpoint inhibitor efficacy against the tumor also varied by donor.
Dr. Hoffmann indicated that the variability in tumor growth and in drug efficacy across different immune cell donors may be a window into understanding drug mechanisms of action and may even help tease out why some patients respond well to these new therapies while others show no response.










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)


.jpg)

.jpg)



