Next-Generation Models enhance the utility of Humanized Immune Model Systems
To meet the growing demands of immunology and oncology research, several next-generation NOG strains have been developed:
- β2m NOG: Supports extended-duration PBMC-engrafted mouse studies by knockout of the murine class I MHC.
- Cytokine-expressing models: These cytokine-enhanced humanized mice offer improved physiological relevance and are particularly valuable for cell therapy and immuno-oncology studies.
- NOG-EXL - Expresses human GM-CSF and IL-3, enhancing the development of both myeloid and lymphoid lineages
- IL-6 NOG - Supports monocytes
- IL-2 NOG - Hematologic malignancies, T cell therapies, CAR-T, and TIL
- IL-15 NOG - NK and CAR-NK
Solving Murine Fc Receptor Interference in Humanized Models
One major challenge in HIS research is the unintended interaction between human antibodies and murine Fc gamma (Fcγ) receptors, which can lead to misleading data in therapeutic antibody studies. To address this, models such as the FcResolv® NOG mouse have been developed. By knocking out murine Fcγ receptors, this strain improves accuracy in antibody efficacy studies and eliminates false positives or negatives.
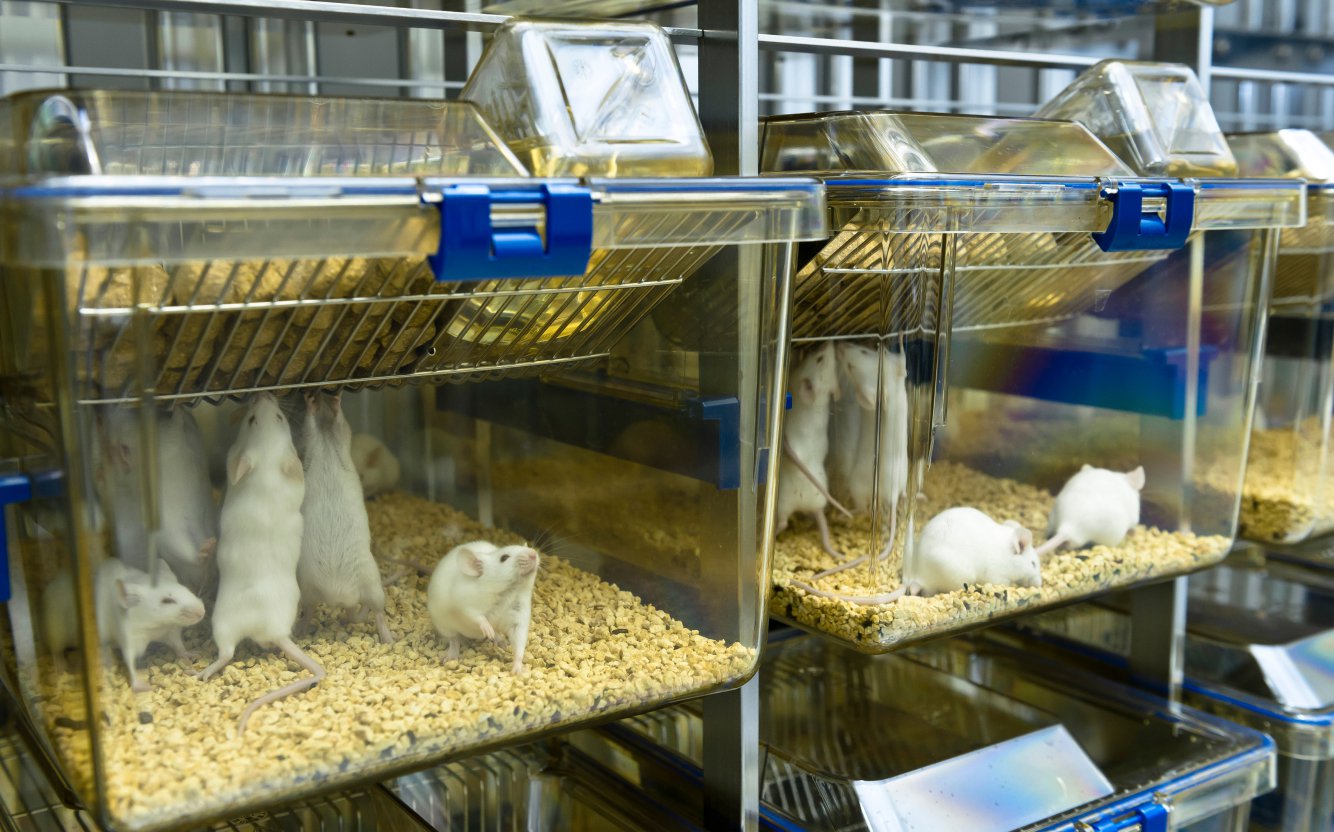
Donor Selection: A Critical Factor in Humanized Immune System Study Design
The source and quality of human donor material significantly impact study reproducibility. To help researchers optimize outcomes, access to pre-validated and pre-characterized CD34+ donors is available:
- Pre-validated donors: Previously engrafted and assessed at 10 weeks for predictable immune reconstitution.
- Pre-characterized donors: Profiled over a 30-week period, offering detailed insights into engraftment kinetics, immune cell composition, and survival rates.
Researchers can also select donors based on HLA type, sex, or ethnicity, enabling personalized and disease-specific modeling, including for GVHD research and HLA-restricted immune responses.
Flexible Humanized Immune System Research Services and Support
To meet diverse research needs, scientists can take advantage of a wide range of customization options and technical support, including:
- Donor material reservation for future studies
- Selection of HLA-typed donors for immune compatibility research
- Custom flow cytometry panel design to evaluate specific immune populations
These capabilities help streamline workflows and enhance study precision.
Conclusion: Humanized Immune System Models as a Foundation for Translational Research
Humanized immune system models are rapidly becoming invaluable in preclinical immunology and immuno-oncology research. With advanced mouse strains, deeply characterized donor options, and customizable research services, these models enable scientists to generate more predictive, human-relevant data.
As the field continues to evolve, humanized mice will remain central to developing next-generation therapies and improving translational outcomes between bench and bedside.
 Key Takeaways
Key Takeaways









.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)




