Application Areas:
Fcgr2b (FcγRII) - Model 580

| Model No. | Nomenclature | Genotype |
|---|---|---|
| 580-F | B6.129S4-Fcgr2btm1TtK N12 | ko/ko |
| 580-M | B6.129S4-Fcgr2btm1TtK N12 | ko/ko |
- Description
- Related Products & Services
- Data
- Price & Licensing
- Health Report
- Overview
- Genetics
- Guides & Publications
- Applications & Therapeutic Areas
- Transit, Housing & Welfare
- Diet
Overview
Nomenclature: B6.129S4-Fcgr2btm1TtK N12
- The mice are deficient in FcgRIIB protein which is a low affinity immunoglobulin G receptor
- The FcgRIIB protein inhibits the activation of disparate effector functions such as phagocytosis, antibody dependent cytotoxicity and release of inflammatory mediators and it is known to function as an inhibitory receptor on B cells and mast cells
- This inhibitory pathway for activation of several immune effector responses is dysfunctional, resulting in the inability to regulate antibody levels in response to antigenic stimuli dependent on IgG immune complexes
- Useful for studying the feedback inhibition pathways that regulate antibody production and in studies of allergic and autoimmune disorders
- The mice are fertile and develop normally
- These mice carry the H2b haplotype
Recommended Controls
The recommended control for this model is C57BL/6NTac.
Origin
The Fcgr2b mouse was developed in the laboratory of T. Takai of Okayama University in 1995. The model was created by targeting the Fcgr2b gene in J1 ES cells. Taconic received pregnant females from Okayama University in November 1996 for use by the laboratory of J.V. Ravetch. Heterozygotes on a hybrid 129 x C57BL/6 background were intercrossed to generate homozygous targeted mutation mice. The mice were then backcrossed twelve generations (N12) to C57BL/6. The mice were derived by embryo transfer and are maintained by incrossing homozygous mice.
Genetics
Guides & Publications
Initial Publication: Takai, T, Ono, M, Hikida, M, Ohmori, H, Ravetch, J. (1996) Augmented humoral and anaphylactic responses in FcgRII-deficient mice. Nature, 379: 346-349.
Applications & Therapeutic Areas
- Autoimmune Disease
- Immunology
- Inflammation
- Oncology & Immuno-Oncology
- Vaccine Research
Transit, Housing & Welfare
Need more info? Click the live chat button or Contact Us
Packing Practices
Taconic standard practice is to recombine animals of different home cages and/or ages from a single model and sex during packing, except in specific cases where Taconic's animal welfare policy prohibits recombination due to aggression or other concerns. When an order is fulfilled with animals from more than one week of birth, this standard practice results in animals from a range of birth weeks packed together in a single TTC. When an order is fulfilled with animals from genotyped models, this standard practice results in animals from different home cages packed together in a single TTC.
Customers who wish to keep animals from different weeks of birth separated should place orders with the special instruction "Divide and label by age." Note that this special request can result in increased costs for additional Taconic Transit Cages, dividers and/or freight charges.
Taconic discourages other types of custom packing requests as they can have a negative impact on animal welfare. Learn more.
Diet
- Services
Data
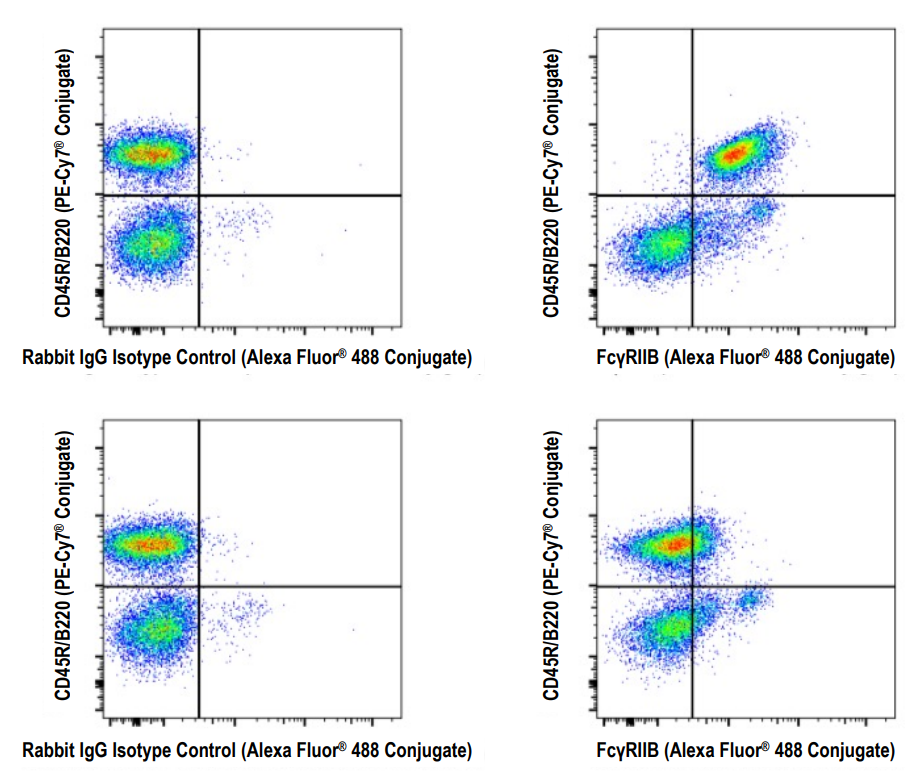
Figure 1: Flow cytometric analysis of fixed and permeabilized splenocytes from wild type C57BL/6NTac (model #B6-F, top) or Fcgr2b knockout (model #580-F, bottom) mice using FcγRIIB (D8F9C) XP® Rabbit mAb (Mouse Specific) (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #54837 (right) or a concentration-matched Rabbit (DA1E) mAb IgG XP® Isotype Control (Alexa Fluor® 488 Conjugate) #2975 (left) co-stained with CD45R/B220 (RA3-6B2) Rat mAb (PE-Cy7® Conjugate) #82922. All antibodies are from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
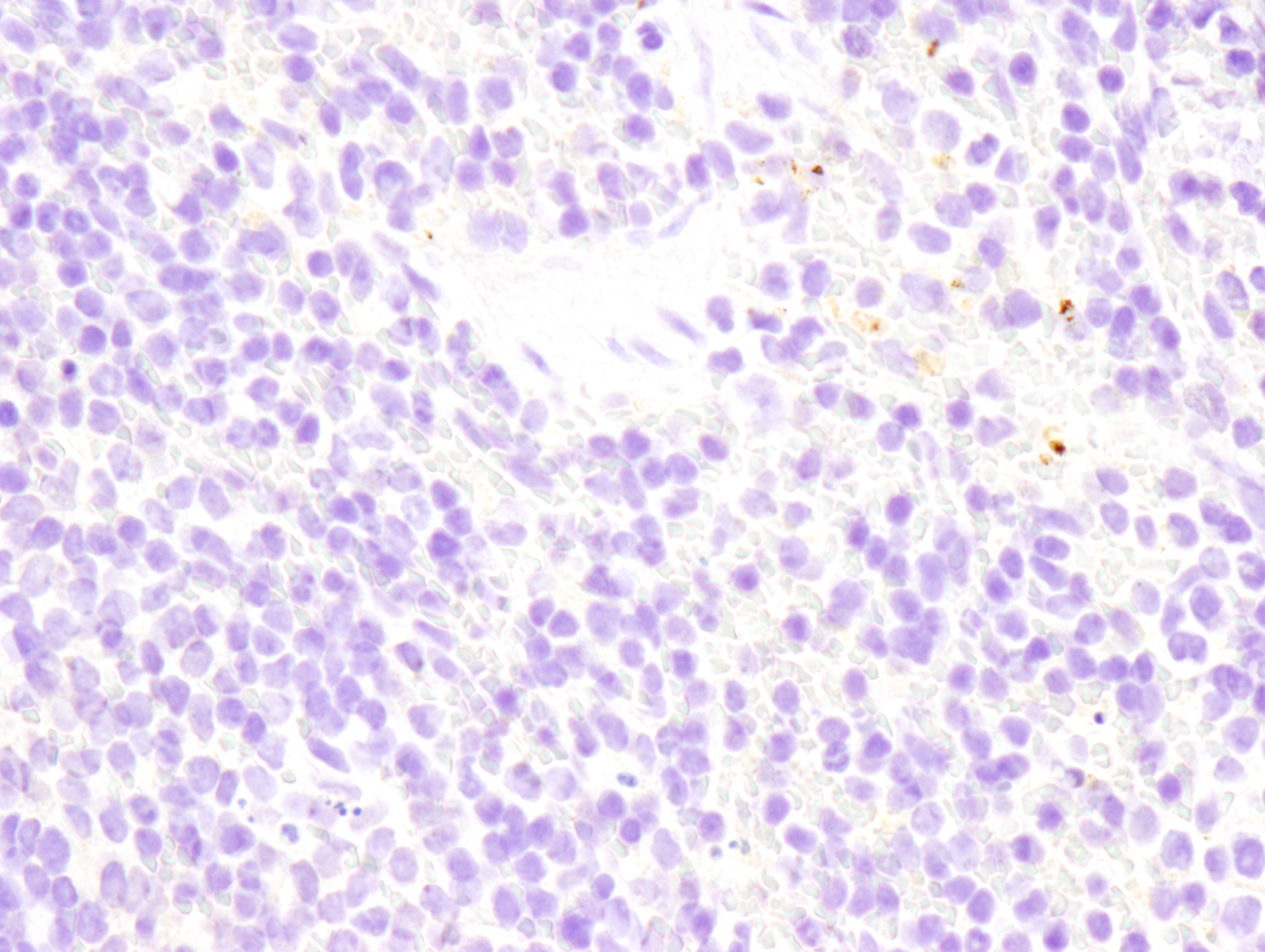 | 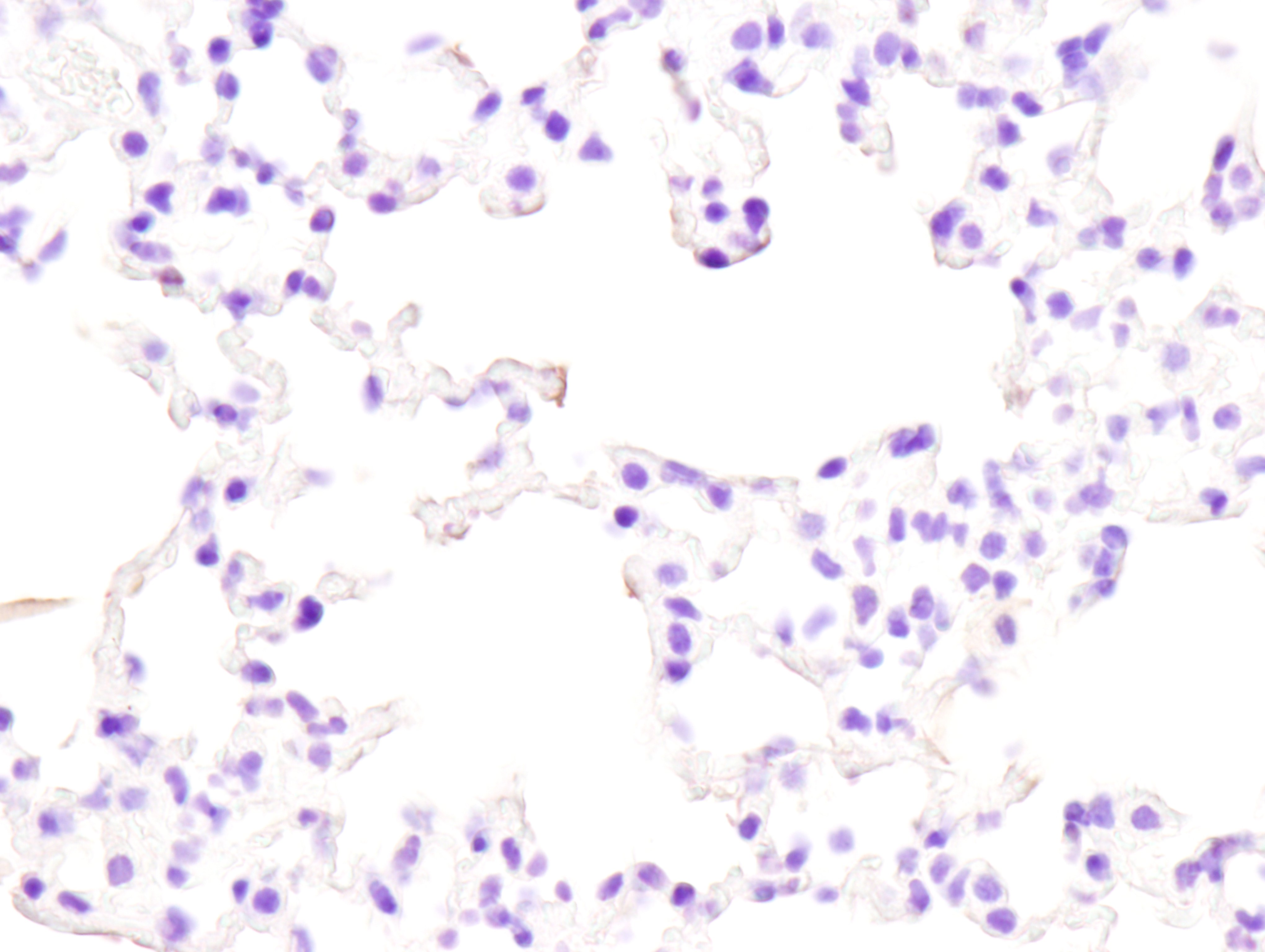 | 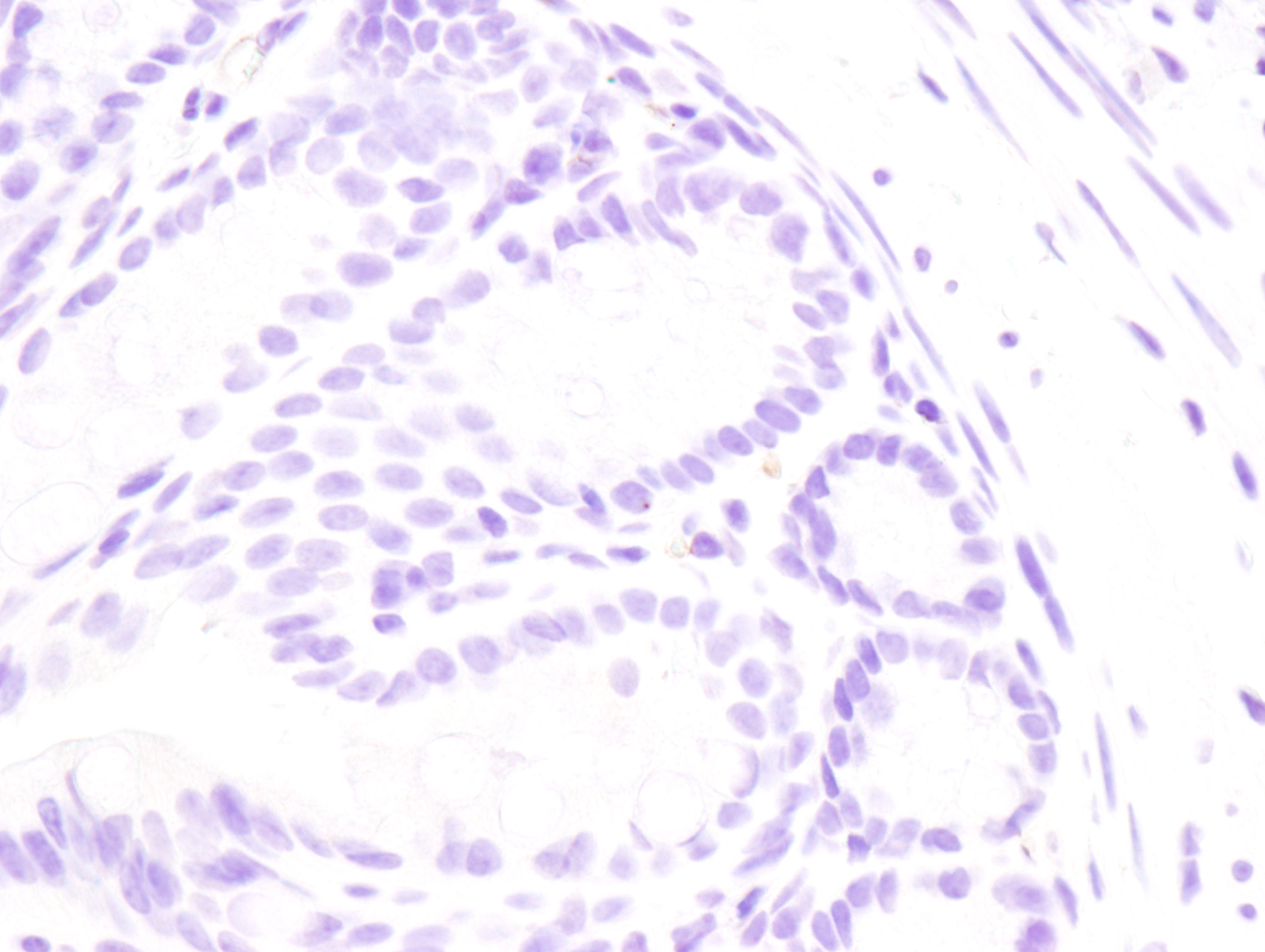 |
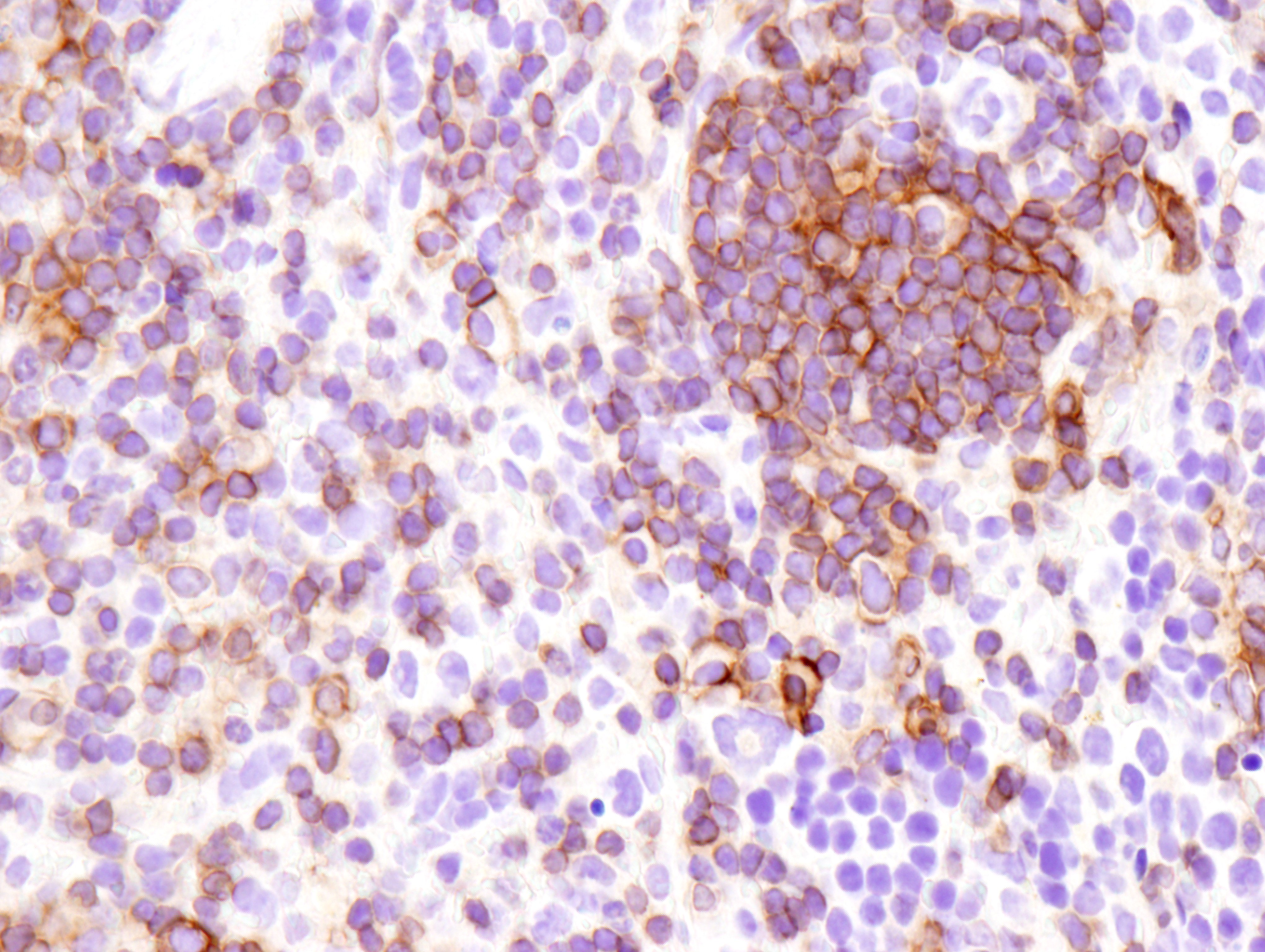
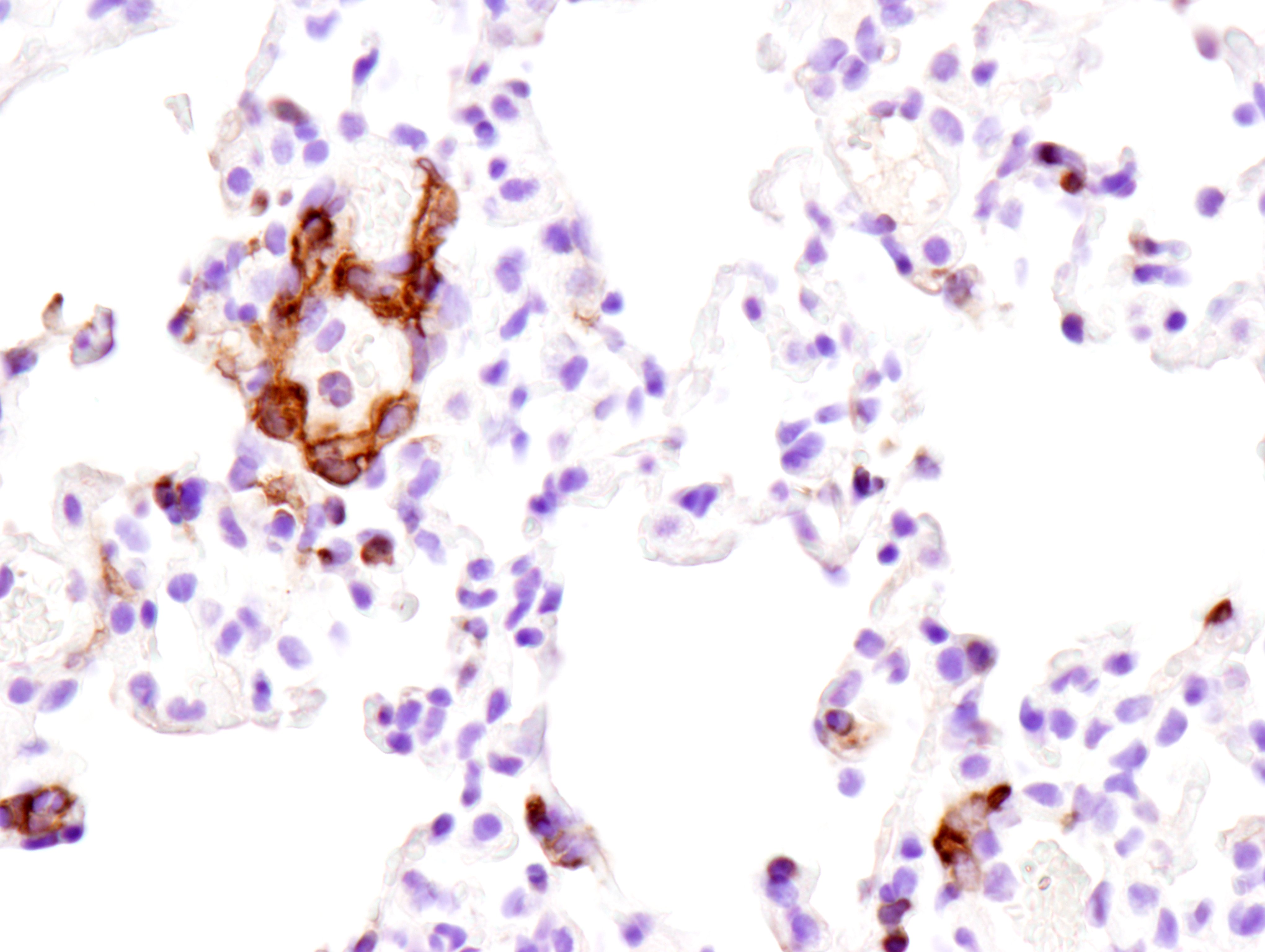
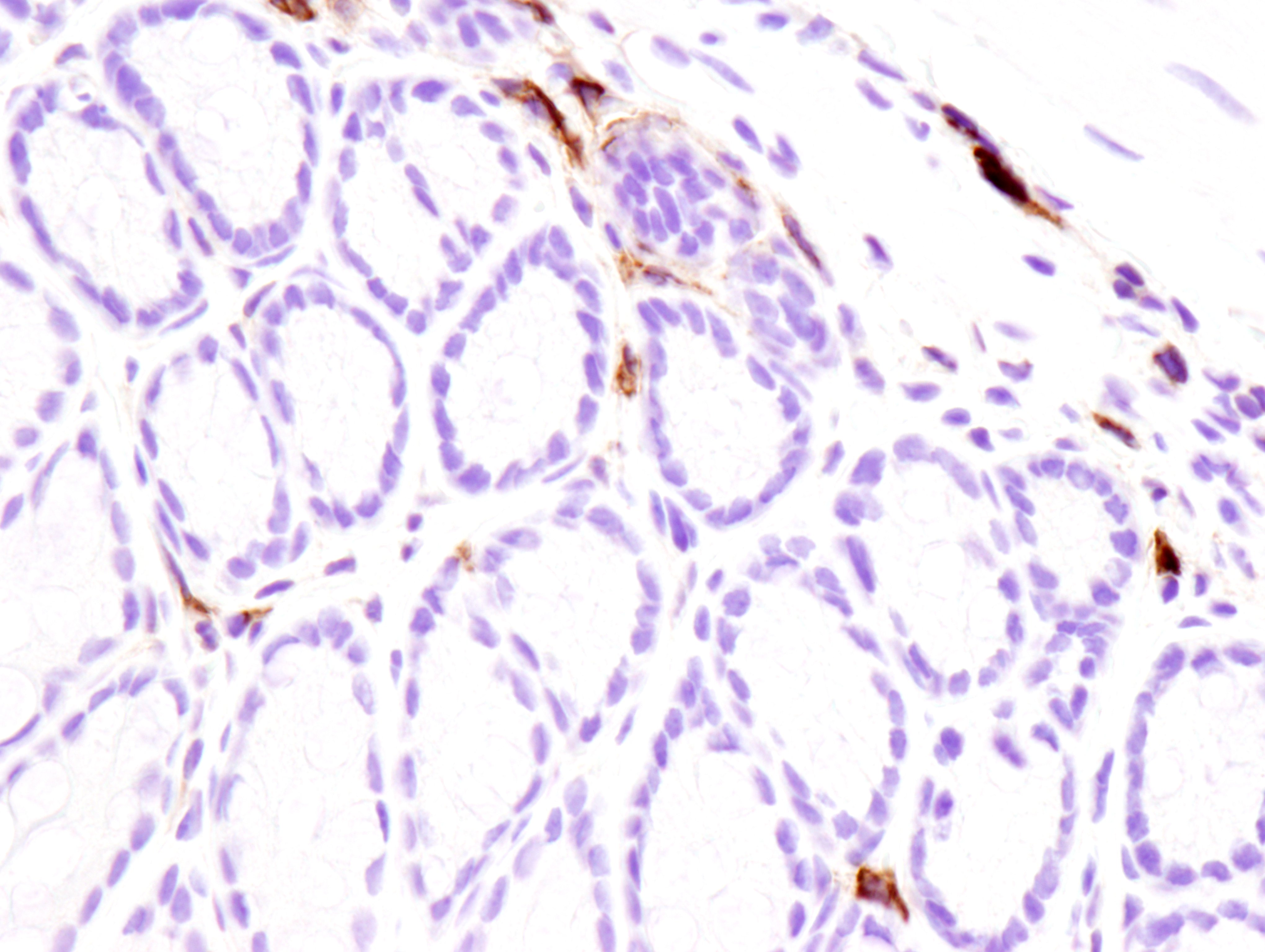
Figure 2: Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse spleen (left), lung (middle) or colon (right) from wild type C57BL/6NTac (model #B6-F, top) or Fcgr2b knockout (model #580-F, bottom) using FcγRIIB (D8F9C) XP® Rabbit mAb (Mouse Specific) #96397 from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
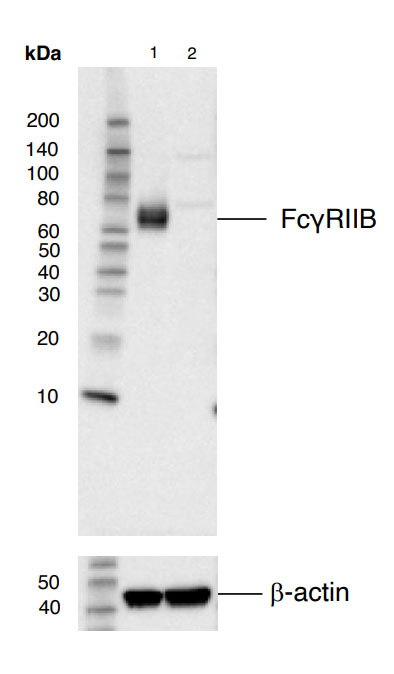 |
Figure 3: Western blot analysis of whole spleen extracts from wild type C57BL/6NTac mice (model #B6-F, lane 1) or Fcgr2b knockout (model #580-F, lane 2) using FcγRIIB (D8F9C) XP® Rabbit mAb (Mouse Specific) #96397 (top) and β-Actin (D6A8) Rabbit mAb #8457 (bottom) from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.
- Licensing
- Pricing - USD
- Pricing - EUR
- Pricing - DKK
- Pricing - USD Nonprofit
- Pricing - EUR Nonprofit
- Pricing - DKK Nonprofit
- Select my Health Standard
- Get Custom Pricing Guide
Fcgr2b (FcγRII) - Model 580
Conditions of Use for Taconic Transgenic Models™
Taconic Transgenic Models™ (Models) are produced and distributed under rights to patents and intellectual property licensed from various institutions. Taconic sells the Models to purchasers, grants to each purchaser a right under Taconic's rights in such licensed patents and intellectual property to use the purchased Model in consideration of purchasers' acknowledgement of and agreement to the Terms and Conditions for Taconic Models, Products and Services and the following terms of use:
- Title to these Models and biological materials derived from them remains with Taconic.
- The Models will be used for research purposes only.
- The Models will not be bred or cross-bred except to obtain embryos or fetuses required for research purposes unless additional rights have been granted in writing by Taconic.
- The Models and biological materials derived from them will not be distributed to third parties or used for commercial purposes.
- Non-profit purchasers may not use this Model and/or biological materials derived from it in sponsored research or contract research studies unless it is purchased at the for-profit price.
Pricing - USD
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | US$449.00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | US$449.00 |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | US$449.00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | US$449.00 |
Pricing - EUR
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | 409,00 € |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | 409,00 € |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | 409,00 € |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | 409,00 € |
Pricing - DKK
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | kr.3.040,00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | kr.3.040,00 |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | kr.3.040,00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | kr.3.040,00 |
Pricing - USD Nonprofit
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | US$396.00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | US$449.00 |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | US$396.00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | US$449.00 |
Pricing - EUR Nonprofit
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | 361,00 € |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | 409,00 € |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | 361,00 € |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | 409,00 € |
Pricing - DKK Nonprofit
Murine Pathogen Free (MPF) Health Standard
580 Female
580-F Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | kr.2.679,00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RF Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired female breeder | kr.3.040,00 |
580 Male
580-M Genotype ko/ko
Cohorts are reserved upon order placement and will take 2-4 weeks to fulfill. An estimated lead time will be provided to you within 2-3 business days.
| Age in Weeks | Quantity 1 - 999 |
|---|---|
| 3 to 10 | kr.2.679,00 |
Specialized Inventory
| 580-RM Genotype ko/ko | Quantity 1 - 199 |
|---|---|
| retired male breeder | kr.3.040,00 |
Select my Health Standard
Need help choosing the right Taconic Biosciences health standard for your research?
Use the Health Standard Selector to enter your exclusion list. The tool will tell you which health standards meet your requirements.
Get custom pricing guide
Schedule A Scientific Consultation
Connect directly with a member of our Scientific Solutions team who can help you select the most appropriate model and maximize your experimental success.










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)