Autophagy in Cellular Processes
Autophagy is derived from Greek and means self(auto)-eating(phagy). This process occurs in all eukaryotic cell types that contain a lysosomal compartment. In fact, basal autophagy contributes to long-lived protein degradation, organelle turnover in the cytoplasm, and the recycling of macromolecules to maintain bioenergetics1.The purpose of autophagy is not solely the simple elimination of materials, but rather the dynamic recycling of cellular components that produces new building blocks and energy for cellular renovation and homeostasis1,2. The process of autophagy is conserved among yeast to mammals.
Macroautophagy begins with the formation of a cup-shaped double membrane structure that engulfs a portion of cytoplasm. This structure then encloses to form a mature vesicle called an autophagosome, which subsequently fuses with a lysosome, leading to the degradation of intra-autophagosomal components by lysosomal enzymes (Figure 1).
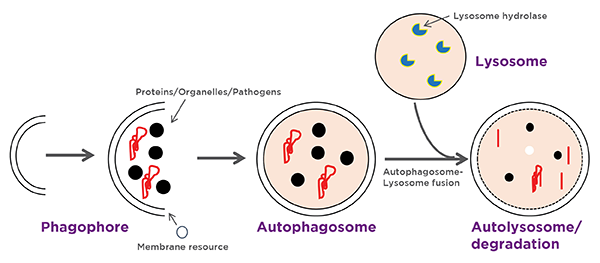
Figure 1
Physiological and Pathological Roles of Autophagy
In mammals there are various diseases which result from impaired autophagy. What follows is a list of diseases associated with dysregulated autophagy2:| Organ-Tissue/Cell type | Role of Autophagy | Disease associated with impaired autophagy |
| All cells-general function | Constitutive autophagy induced by starvation resulting in degradation of cytoplasmic contents into simpler production | Aging, cell death2, cancer3 |
| Brain-neurons & microglia | Prevention of protein aggregate formation, mitochondria degradation in microglial cells and neurons | Parkinson's disease4 Alzheimer's disease4 |
| Liver-hepatocytes | Prevention of hepatocytes degradation; suppression of tumors | Hepatocellular carcinoma2 |
| Bone marrow-macrophages, dendritic cells, monocytes | Maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells, degradation of intracellular pathogens | Microbial Infection and impaired immunity5 |
| Lymphoid system | Regulation of cytokine production | Microbial infection5 |
| Pancreas- islets of langerhans | B-cell adaptation to high fat diet | Diabetes2 |
| Adipose tissues | Adipogenesis | Obesity2 |
| Intestine-paneth cells | Aberrant expression of inflammatory cytokines | Crohn's disease2 |
Murine Models to Study Autophagy
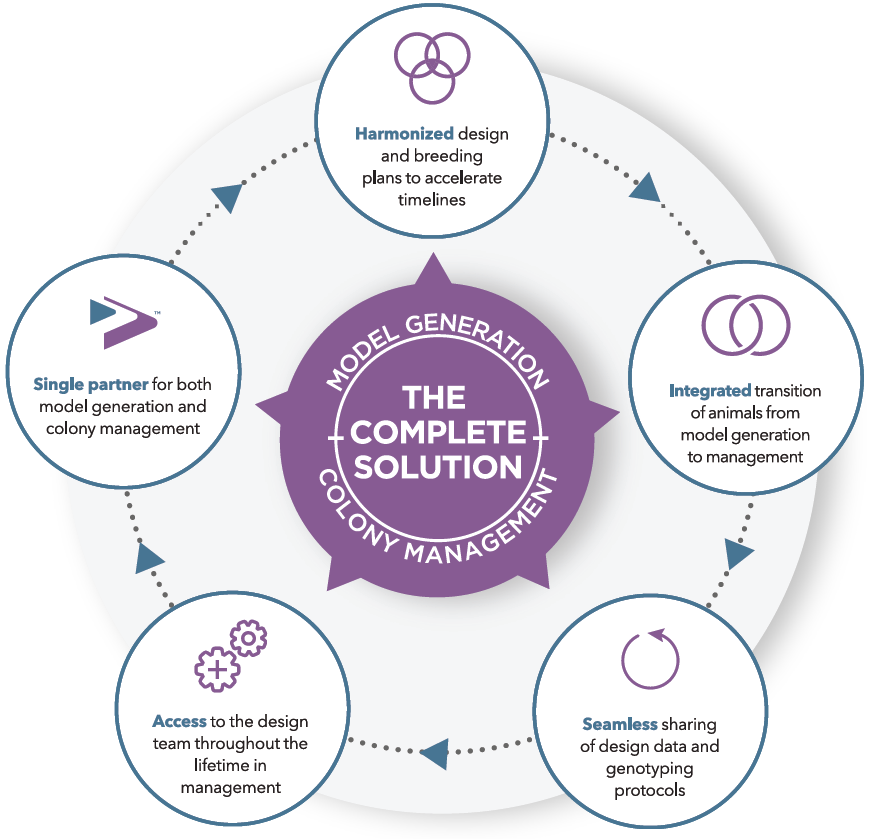
One of the contributing factors for the increased knowledge of physiological roles of autophagy is availability of mouse models to study autophagy. Essentially, two types of gene-modified mouse models have played critical roles: "autophagy-monitoring mice"6 and "autophagy-deficient mice"7. Monitoring the autophagic process and measuring autophagic flux in different tissues and organelles is critical to investigate the function of autophagy under specific stimuli. Analysis of autophagy-deficient mice has led to conceptual findings in this field.Taconic Biosciences offers various murine models to study diverse aspects of autophagy in different cell types.
| Mouse Model | Taconic Model # | Roles in Autophagy |
| Atg4b KO | TF2950 | Atg4b is a member of ATG4-family cysteine proteases. These proteases have an important function as an essential factor in the Atg8 conjugation and deconjugation system, one of the unique mechanisms in autophagy. Inhibition of Atg4b results in inhibition of autophagy8. |
| Atg4c KO | TF2255 | Atg4c is a member of ATG4-family cysteine proteases8. |
| Atg4d KO | TF1385 | Atg4d is a member of ATG4-family cysteine proteases8. |
| TNFα Tg | 1006 | Tnfα induced autophagy play a critical role in induction of apoptosis/cell death in placental cells during pregnancy. Induction of autophagy has been implicated in placental dysfunction during pregnancies9. TNFα induce autophagy in vitro and in vivo in osteoclasts of human rheumatoid arthritis (RA) thus regulating osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption and play a central role in RA10. |
| SumF1 KO | TF3462 | Deficiency of SumF1 is associated with lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) which results in severe neurodegeneration due to inability of degradation of intracellular proteins by the process of autophagy11. |
| Dram 2 KO | TF3276 | Dram-2 interacts with central protein of autophagy LC3 to enhance autophagosome formation in DPN-mediated estrogen receptorβ activated autophagy in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) cells. The induction of autophagy reduces 60% growth of lymphoma cells by inhibiting cell proliferation3. |
| Nlrp3 KO | 12935 | Autophagy keeps NLRP3 inflammasome activation in check by degrading oxidized mitochondria in macrophages thus limiting the NLRP3 inflammasome driven auto-inflammatory chronic inflammation12. |
| Pik3c3 KO | TF1967 | Pik3c3 play a crucial role in mTOR driven autophagic lysosome reformation (ALR). Defects in the ALR process results in increase neuronal death13. |
| 2045 | 2045 | Stat1 inhibits autophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblasts by transcriptional inhibition of the expression of a key autophagy protein ULK114. |
| CIEA NOG mouse ® | NOG | NOG mice were used to demonstrate the role of QSOX1 protein (Quiescin Sulfhydryl oxidase) in inhibiting tumor growth and progression in breast cancer cells by downregulating autophagy15. |










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)


.jpg)

.jpg)



