Tbk1 and ALS
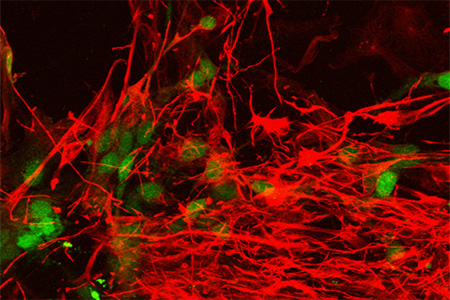
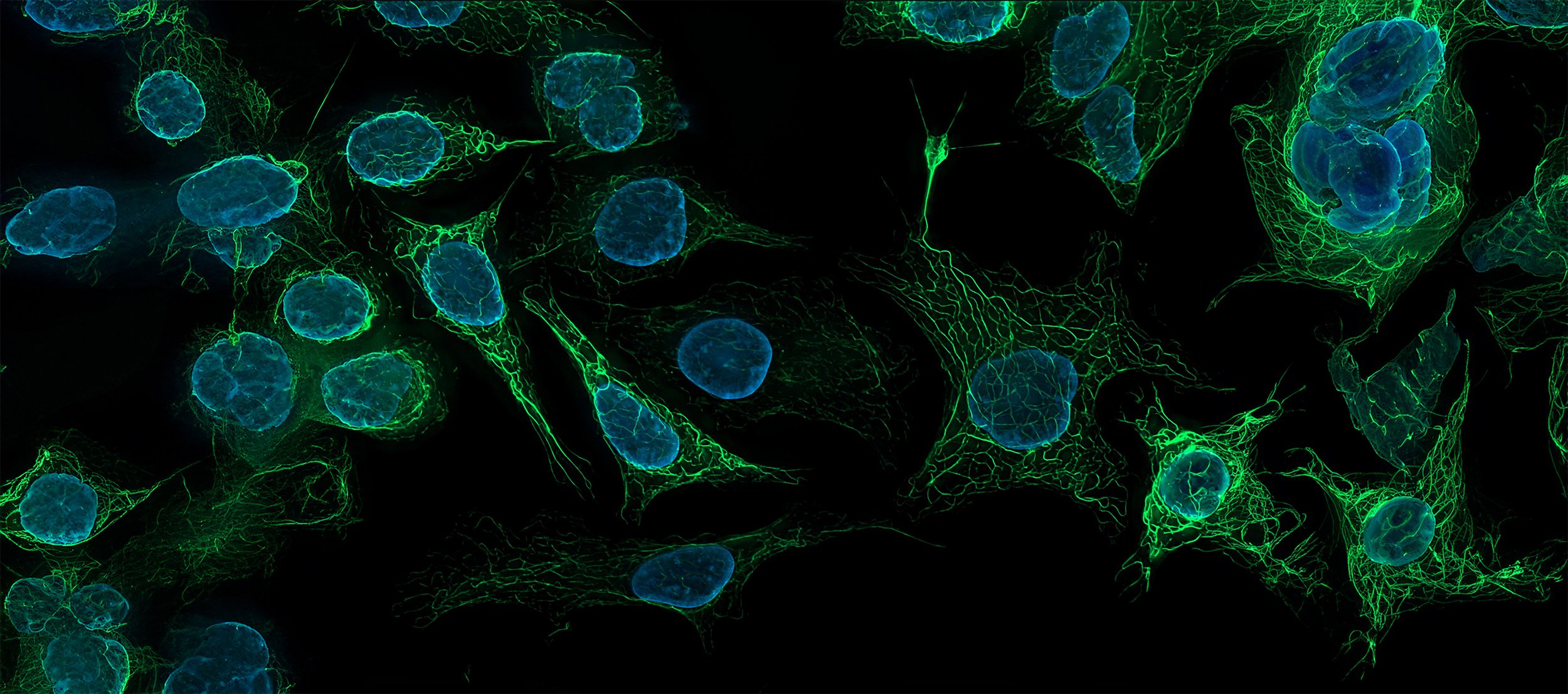
Image shows iPS derived motor neurons from an ALS patient.
Tuj 1 ab shown in red and Hb9 ab in green.1
Image shows iPS derived motor neurons from an ALS patient.
Tuj 1 ab shown in red and Hb9 ab in green.1
Tbk1 background
Tbk1 was known as a regulator of the innate immune system, but its specific in vivo roles were difficult to ascertain due to the reported embryonic lethality of a null mutation. Knockdown and over expression studies confirmed Tbk1's role in regulating the immune system, but more precise mechanistic studies were needed. In 2012, Jin et.al. used a conditional Tbk1 model to reveal a new and exciting role for Tbk1 in IgA class switching2. The group was interested in studying the in vivo function of Tbk1 in regulating humoral immune responses. To create a B-cell specific ablation of Tbk1 function, they crossed the conditional Tbk1 line to CD19-Cre mice. They were able to determine that the B cell-specific KO of Tbk1 did not affect B cell development or maturation and therefore allowed the study of Tbk1's role in B cell activation and differentiation. This use of the conditional Tbk1 mutants led to the surprising discovery that Tbk1 plays a role in the control of IgA class switching. Tbk1 was found to inhibit IgA class switching by opposing the signals from tumor necrosis factor (TNF ) family members. This remarkable discovery in a complex, multi-step process required the use of a suitable animal model.New role for Tbk1 defined
The functions of the Tbk1 gene have been an active area of research for many years. As we have seen, more recent studies have precisely defined Tbk1's role in innate immunity using a reverse genetic approach (gene to phenotype). Of course, another way to approach defining gene function is by analyzing existing phenotypes and determining the causative mutation(s). With the advent of high throughput, low cost whole genome sequencing, this forward genetic approach is proving to be increasingly powerful. This year, a new role for Tbk1 was defined opening up an entirely new area of research.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative syndrome hallmarked by adult-onset loss of motor neurons. In the paper, Haploinsufficiency of TBK1 causes familial ALS and fronto-temporal dementia, Freischmidt et. al. performed whole exome sequencing of 252 familial ALS patients3. Sequence comparison to control individuals identified significant enrichment of loss-of-function mutations in TBK1 in multiple pedigrees. This surprising discovery opened up an entirely new research focus around the Tbk1 gene and gives new hope to patients suffering from the devastating ALS disease.










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)



