| Model No. | Nomenclature | Genotype |
|---|---|---|
| 1486 | FVB.129P2-Abcc1atm1Bor N12 | Inquire for genotype |
Mrp1
- Description
- Related Products & Services
- Price & Licensing
- Overview
- Genetics
- Guides & Publications
- Applications & Therapeutic Areas
- Transit, Housing & Welfare
- Diet
Overview
Nomenclature: FVB.129P2-Abcc1atm1Bor N12
- Carries a disruption of the Abcc1a (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C (CFTR/MRP), member 1a) gene that encodes an ATP-dependent drug-extruding transporter formerly known as Mrp1
- Abcc1a encodes ATP-dependent transport proteins for glutathione-, glucuronide-, or sulfate-conjugated substrates, including endogenous compounds such as steroids and leukotrienes as well as xenobiotics drugs
- One of a family of ATP-binding cassette genes which encode multi-drug resistance proteins which confers resistance to a range of cytotoxic drugs
- Exhibits normal fertility and viability but is deficient in functional MRP1 protein, leading to a 95% reduction in cellular transport of glutathione-conjugated substrates and decreased transport of leukotrienes C4, known inflammatory mediators
- Exhibits an impaired inflammatory stimulus response and hypersensitivity to the anti-cancer drug, etoposide and vincristine
- Useful for studying the role of ATP-dependent transporters in mediating inflammatory response and to test drug disposition
Origin
The Mrp1 mouse was developed in the laboratory of Piet Borst at the Netherlands Cancer Institute. The model was created by targeting the Abcc1a gene in 129/Ola derived E14 ES cells and injecting the targeted cells into blastocysts. Resultant chimeras were backcrossed to FVB/N for six generations (N6). Taconic received stock in 1999. After additional backcrosses to FVB/NTac to N12, the line was embryo derived. Heterozygotes were intercrossed to generate homozygotes. The colony was maintained through incrossing of homozygous mice.
This model is cryopreserved and available for recovery. Models can typically be recovered and delivered to customers within 12 weeks after order receipt. Purchase of this model includes perpetual use rights and a deliverable of four mutant animals at the Murine Pathogen Free™ health standard along with a genotyping protocol. For models which include a recombinase gene or multiple alleles, all alleles will be provided, but individual animals may not contain all mutant alleles.
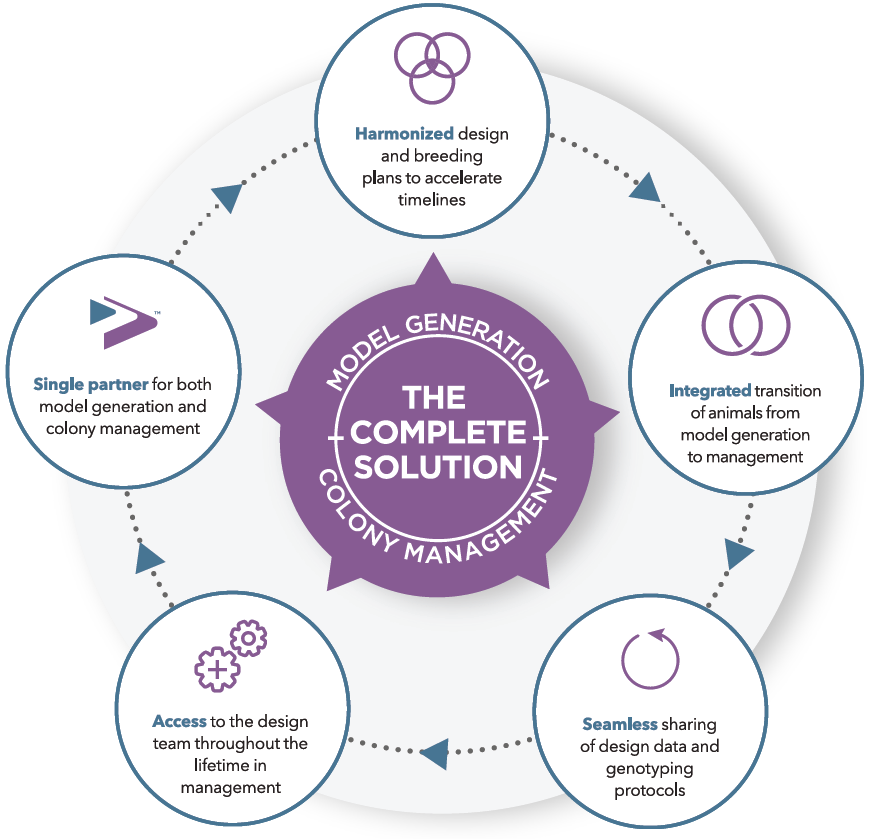
Taconic’s Colony Management experts can design a plan to grow your colony faster.
Genetics
Guides & Publications
Initial Publication:
Wijnholds J, Evers R, van Leusden MR, Mol CAAM, Zaman GJR, Mayer U, Beijnen JH, van der Valk M, Krimpenfort P, Borst P. (1997) Increased sensitivity to anticancer drugs and decreased inflammatory response in mice lacking the multidrug resistance-associated protein.; Nature Med, 3:1275-9.
Applications & Therapeutic Areas
- ADMET
Transit, Housing & Welfare
Need more info? Click the live chat button or Contact Us
Diet
- Services
- Licensing
- Pricing - USD
- Pricing - EUR
- Pricing - DKK
- Select my Health Standard
- Get Custom Pricing Guide
Mrp1
This model is sold under terms which grant perpetual use rights.
Pricing - USD
1486-EZcohort-4
| Item | Commercial | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | US$14,000.00 | US$14,000.00 |
Cryopreserved models are invoiced upon shipment of recovered animals. Once orders are placed, the full purchase price will be applied if the order is canceled. For orders greater than 4 animals, please contact Taconic for options.
Fees for Taconic Transit Cages™ and freight are in addition to the price above.
Pricing - EUR
1486-EZcohort-4
| Item | Commercial | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | 12.100,00 € | 12.100,00 € |
Cryopreserved models are invoiced upon shipment of recovered animals. Once orders are placed, the full purchase price will be applied if the order is canceled. For orders greater than 4 animals, please contact Taconic for options.
Fees for Taconic Transit Cages™ and freight are in addition to the price above.
Pricing - DKK
1486-EZcohort-4
| Item | Commercial | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | kr.90.266,00 | kr.90.266,00 |
Cryopreserved models are invoiced upon shipment of recovered animals. Once orders are placed, the full purchase price will be applied if the order is canceled. For orders greater than 4 animals, please contact Taconic for options.
Fees for Taconic Transit Cages™ and freight are in addition to the price above.
Select my Health Standard
Need help choosing the right Taconic Biosciences health standard for your research?
Use the Health Standard Selector to enter your exclusion list. The tool will tell you which health standards meet your requirements.
Get custom pricing guide
Schedule A Scientific Consultation
Connect directly with a member of our Scientific Solutions team who can help you select the most appropriate model and maximize your experimental success.










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)








