| Model No. | Nomenclature | Genotype |
|---|---|---|
| TF3738 | MGI:1917258 | Inquire for genotype |
Ace2
- Description
- Data
- Price & Licensing
- Overview
- Genetics
- Guides & Publications
- Transit, Housing & Welfare
Overview
Nomenclature: MGI:1917258
- ARDS is a serious complication of COVID-19 and present in a large percentage of COVID-19 deaths. ACE2 is protective against ARDS.
- Binding of viral spike SARS protein to ACE2 in mice downregulates ACE2 expression. Loss of ACE2 expression is associated with severe lung failure. Ace2 knockout mice have been used in ARDS and SARS research.
- This model does NOT carry the human ACE2 gene and thus is likely not permissive for infection by clinical isolates of SARS-CoV-2. Taconic has mice that express human ACE2 (hACE2) available now. Learn more about hACE2 mice for COVID-19 research and mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 viruses.
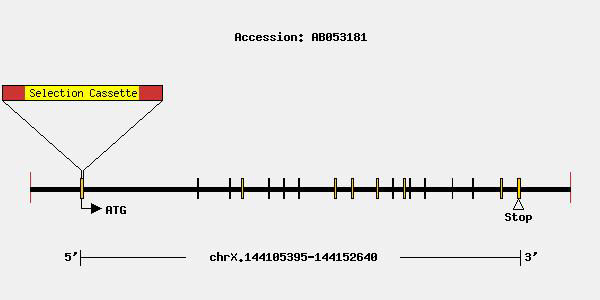
- The Ensembl database shows two isoforms of mouse ACE2 protein, one starting from Exon 2 of the gene (805 aa) and the second starting from Exon 6 (521 aa). The modification in this model targets the second exon (first coding exon) of Ace2, which is expected to result in a loss-of-function allele for the full-length isoform. It is unknown whether the second isoform will be produced in this model and if produced whether it is functional or not and can compensate for the loss of the full-length isoform. Correct targeting of the allele was confirmed by Southern blot analysis. Several publications have described phenotypic differences between wild type and homozygous mutant animals for this modification, consistent with interference with Ace2 function. It is recommended that researchers confirm loss-of-function status of the allele in their experimental system or tissue of interest.
- This line was generated on a mixed genetic background (B6;129S5). Researchers should be aware that phenotypes such as hypertension may vary for specific Ace2 knockout alleles on different inbred genetic backgrounds (Gurley and Coffman, 2007). Thus, as the result of a mixed genetic background the Ace2 knockout mice may show considerable inter-animal variation in phenotypes. It is recommended to carefully consider the impact of the genetic background when planning and interpreting experiments. Taconic can advise on backcross strategies and provide testing for marker-assisted speed congenic breeding. Generation of a fully congenic line can take 12-18 months.
- The murine Ace2 gene is located on the X chromosome. Female knockouts are homozygous (ko/ko). Male knockouts are hemizygous (ko/y).
Synonyms: 2010305L05Rik
This model is cryopreserved and available for recovery. Models can typically be recovered and delivered to customers within 12 weeks after order receipt. Purchase of this model includes perpetual use rights and a deliverable of four mutant animals at the Murine Pathogen Free™ health standard along with a genotyping protocol. For models which include a recombinase gene or multiple alleles, all alleles will be provided, but individual animals may not contain all mutant alleles.
For most Knockout Repository lines, the mouse ES cells used in generating the model are of the 129S5 strain. Lines are stored primarily as cryopreserved sperm on a mixed 129S5 x C57BL/6J- Tyrc-Brd background. Lines are recovered using cryopreserved sperm and C57BL/6NTac oocyte donors. Some lines are stored as cryopreserved embryos and when revitalized will result in a 129S5 x C57BL/6J- Tyrc-Brd
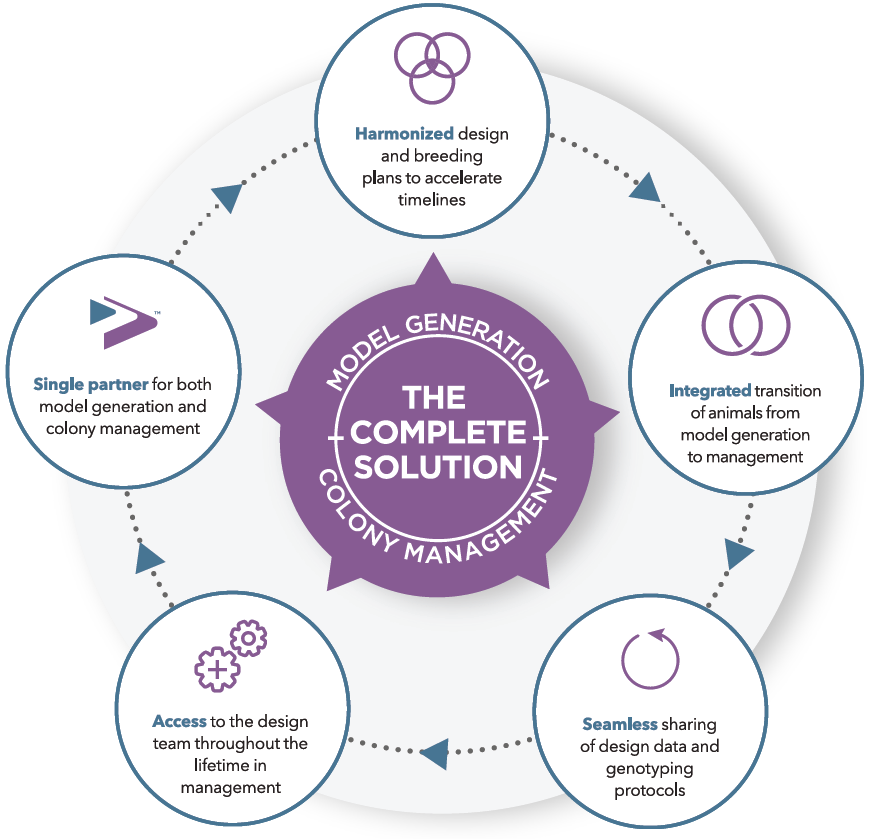
Taconic’s Colony Management experts can design a plan to grow your colony faster.
Genetics
Guides & Publications
Transit, Housing & Welfare
Need more info? Click the live chat button or Contact Us
Data
- Terms of Sale
- Pricing
- Select my Health Standard
- Get Custom Pricing Guide
USD
| Item | Commercial | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | $21,000 | $13,000 |
| Basic Phenotype Package | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Comprehensive Phenotype Data | $8,000 | $6,000 |
If you choose to breed this model at Taconic, you are eligible for a 20% discount on the repository model price and a 50% discount on the data package price as outlined below.
| Item | Commercial (with breeding discount) | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | $16,800 | $10,400 |
| Basic Phenotype Package | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| Comprehensive Phenotype Data | $4,000 | $3,000 |
EUR
| Item | Commercial | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | €21.000 | €13.000 |
| Basic Phenotype Package | €3.000 | €3.000 |
| Comprehensive Phenotype Data | €8.000 | €6.000 |
If you choose to breed this model at Taconic, you are eligible for a 20% discount on the repository model price and a 50% discount on the data package price as outlined below.
| Item | Commercial (with breeding discount) | Nonprofit |
|---|---|---|
| Cryopreserved Model | €16.800 | €10.400 |
| Basic Phenotype Package | €1.500 | €1.500 |
| Comprehensive Phenotype Data | €4.000 | €3.000 |
Data packages may be purchased with no requirement to purchase the related model.
Cryopreserved models are invoiced upon shipment of recovered animals. Once orders are placed, the full purchase price will be applied if the order is canceled. For orders greater than 4 animals, please contact Taconic for options.
Fees for Taconic Transit Cages™ and freight are in addition to the price above.
Select my Health Standard
Need help choosing the right Taconic Biosciences health standard for your research?
Use the Health Standard Selector to enter your exclusion list. The tool will tell you which health standards meet your requirements.
Get custom pricing guide
Schedule A Scientific Consultation
Connect directly with a member of our Scientific Solutions team who can help you select the most appropriate model and maximize your experimental success.










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)



