Syngeneic mouse models are important preclinical research tools for immuno-oncology drug discovery. Tumors engrafted into these models are not rejected by the host and thereby enable researchers to investigate new drugs in the context of a fully functioning immune system. Taconic offers a range of syngeneic tumor hosts from popular inbred strains to advanced genetically engineered models. Additionally, our syngeneic cell line database can be used to identify tumor cell lines, their associated background strains, and select the most appropriate model for your study.
Syngeneic Tumor Mouse Models

Syngeneic Tumor Model Generation
To generate a syngeneic tumor model, a murine tumor cell line that originated in an inbred strain is first cultured in vitro and then implanted into mice of the same genetic background. A key advantage of this type of tumor model is that the host has a competent immune system, which is required to evaluate immune-modulating drugs.

Advantages of Syngeneic Mouse Models For Immuno-Oncology Research
- Fully intact immune system
- Tumor, immune system, and stroma are genetically matched
- Compatible with existing and custom GEMs enabling greater flexibility
- Germ-free and gnotobiotic inbred strains available for microbiome studies
- Genetically engineered Jh Mouse enables researchers to conduct syngeneic studies without the negative effects of immunogenicity
Standard Inbred Strain Used as Hosts For Syngeneic Tumor Experiments
Taconic offers key inbred strains at multiple health standards, including Germ Free, to facilitate oncology studies with a microbiome component.
| Strain | Taconic Models | Notes |
| C57BL/6 | C57BL/6NTac | Th1 immune bias. B6 and BALB/c are the two most commonly used strain backgrounds for syngeneic tumor studies. Cohorts of aged female retired breeders are available to study the intersection of cancer and aging. Some lead time required. Cohort may have an expanded age range. |
| C57BL/6JBomTac | ||
| BALB/c | BALB/cAnNTac | Th2 immune bias. B6 and BALB/c are the two most commonly used strain backgrounds for syngeneic tumor studies. Cohorts of aged female retired breeders are available to study the intersection of cancer and aging. Some lead time required. Cohort may have an expanded age range. |
| BALB/cJBomTac | ||
| C3H | C3H/HeNTac | |
| DBA/2 | DBA/2NTac | |
| FVB | FVB/NTac | Primarily used for mammary tumor studies. |
| DBA/1 | DBA/1JBomTac | |
| 129S6 | 129S6/SvEvTac |
Taconic has compiled a database of published syngeneic tumor cell lines, with details on cancer type, strain background, immunogenicity and metastatic potential. Filter or search by any of these characteristics to identify relevant cell lines for your research.
The Jh Mouse
Antibody-deficient C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice for immuno-oncology research.
The Jh Mouse permits clinically-relevant dosing of immunogenic test articles in syngeneic tumor model systems.
Standard Inbred Strain



BALB/c mouse
Implemented with syngeneic tumor cell line derived from BALB/c or
C57BL/6 mouse
Implanted with syngeneic tumor cell derived from C57BL/6
Standard inbred host develops humoral immune response (anti-drug antibodies) against test article, which can neutralize the therapy or even cause anaphylaxis.
Jh Mouse
The Jh Mouse may be crossbred to other GEM strains, such as genetically humanized PD-1 mice to further extend the utility of this system. Inquire for details on crossbreeding rights.



Jh Mouse implanted with syngeneic tumor cell line derived from BALB/c or C57BL/6
Taconic offers two Jh models:
- Jh Mouse of BALB/c background (model #1147)
- Jh Mouse on C57BL/6 background (model #17758)
The Jh Mouse lacks B cells, so no anti-drug antibodies are produced. It retains other immune cell types such as T cells, so immunotherapies can be successfully evaluated using clinically-relevant dosing.
C57BL/6 Suite of Strains For Syngeneic Tumor Modeling
| Strain | Strain Type | Immunodeficiencies | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| C57BL/6NTac | Inbred | None | Inbred strain. B6/N substrain. Widely available in North America and Europe. |
| C57BL/6JBomTac | Inbred | None | Inbred strain. B6/J substrain. Widely available in Europe. |
| B6.SJL-Ptprca | Adoptive Transfer | None | Congenic on C57BL/6NTac. Carries the SJL-derived Ptprca (Cd45.1/Ly5.1) allele, which can be used to distinguish between transferred lymphocytes derived from this donor strain and C57BL/6NTac recipient mice. |
| β-actin-luc | Adoptive Transfer | None | Reporter strain with constitutive expression of luciferase in all tissues tested. May be used as source of luciferase-labeled donor cells for adoptive transfer into C57BL/6 recipient mice. |
| Rag2/OT-I | TCR Transgenic | Does not develop mature T or B cells expressing endogenous T cell receptors. | Useful as either a tumor recipient or as a source of homogenous donor CD8+ T cells for in vivo adoptive transfer studies to investigate MHC class I-restricted CD8+ T cell responses to ovalbumin-expressing tumors. |
| Rag2/OT-II | TCR Transgenic | Does not develop mature T or B cells expressing endogenous T cell receptors. | Useful as either a tumor recipient or as a source of homogenous donor CD4+ T cells for in vivo adoptive transfer studies to investigate MHC class II-restricted CD4+ T cell responses to ovalbumin-expressing tumors. |
| Jh (C57BL/6) | Immunodeficient | Lacks B cells | B cell-deficient but retains other immune cell types such as T cells and myeloid cell populations. Useful for studying immunotherapies that could induce ADA and/or anaphylaxis in wild type mice. |
| Rag2 Knockout | Immunodeficient | Lacks T and B cells | Tumors may grow more quickly in an immunodeficient host. Amenable to adoptive transfer of immune cells from C57BL/6NTac or other C57BL/6 lines. |
| Rag2/Il2rg Knockout | Immunodeficient | Lacks T, B and NK cells; dysfunctional dendritic cells. | Tumors may grow more quickly in an immunodeficient host. Amenable to adoptive transfer of immune cells from C57BL/6NTac or other C57BL/6 lines. |
| Abb Knockout | Immunodeficient | Expresses no A or E MHC class II molecules and therefore lacks most CD4+ T cells. | Useful for mechanistic studies of the immune response by eliminating CD4+ T cell responses. |
| Abb Knockout with Ptprca | Immunodeficient | Expresses no A or E MHC class II molecules and therefore lacks most CD4+ T cells. | Useful for mechanistic studies of the immune response by eliminating CD4+ T cell responses. Carries the SJL-derived Ptprca (Cd45.1/Ly5.1) allele, which can be used to distinguish between transferred lymphocytes derived from this donor strain and C57BL/6NTac recipient mice and vice versa. |
| B2m Knockout* | Immunodeficient | Deficient in MHC Class I molecule expression and exhibits depletion of CD8+ and NK1.1+ CD4+ T cells. | Useful for mechanistic studies of the immune response by eliminating CD8+ T cell responses. Note: may also show decreased immunoglobulin half life in this model due to decreased FcRn expression. |
| Abb/B2m Knockout* | Immunodeficient | Expresses no A or E MHC class II molecules and therefore lacks most CD4+ T cells. Deficient in MHC Class I molecule expression and exhibits depletion of CD8+ and NK1.1+ CD4+ T cells. | Useful for mechanistic studies of the immune response by eliminating both MHC class I and II signaling. |
| Fcer1g (FcRγ) | Immunodeficient | Deficient in the gamma chain subunit of the FcgRI, FcgRIII and FceRI receptors, resulting in functionally impaired macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, basophils and NK cells. | Useful for studies to distinguish the role of the Fc receptors in antibody-mediated effector responses and to evaluate the contribution of IgG and IgE triggered effector pathways. |
| Fcgr2b (FcyRII) | Immunodeficient | Deficient in FcgRIIB protein, a low affinity immunoglobulin G receptor which inhibits the activation of disparate effector functions such as phagocytosis, antibody dependent cytotoxicity and release of inflammatory mediators. | Useful in mechanistic studies by removing the inhibitory function of FcgRIIB, or in identifying antibody-mediated FcgRIIB-dependent crosslinking effector mechanisms. |
*Available from Taconic's cryopreserved repository.
Transgenic HLA Mice For Syngeneic Tumor Models
Note: Syngeneic tumor take rate and growth kinetics may vary between wild type and immunodeficient mice on the same strain background. A pilot study is always good practice to assess cell line choice and experimental conditions prior to a full study.
BALB/c Suite of Strains For Syngeneic Tumor Modeling
| Strain | Strain Type | Immunondeficiencies | Relevance to Syngeneic Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| BALB/cAnNTac | Inbred | None | Inbred strain. |
| BALB/cJBomTac | Inbred | None | Inbred strain. |
| Jh (BALB/c) | Immunodeficient | Lacks B cells | B cell-deficient but retains other immune cell types such as T cells and myeloid cell populations. Useful for studying immunotherapies that could induce ADA and/or anaphylaxis in wild type mice. |
| Fcer1g (FcRγ) | Immunodeficient | Deficient in the gamma chain subunit of the FcgRI, FcgRIII, and FceRI receptors. Macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, and NK cells are functionally impaired, due to the lack of these Fc receptors. | Useful in determining the role of structurally similar Fc receptors in mediating effector immune responses and studying the pleiotropic role of the g chain subunit. |
| Fcgr2b (FcγRII) | Immunodeficient | Deficient in the FcgRIIB protein, resulting in the inability to regulate antibody levels in response to antigenic stimuli dependent on IgG immune complexes. | Useful in mechanistic studies by removing the inhibitory function of FcgRIIB, or in identifying antibody-mediated FcgRIIB-dependent crosslinking effector mechanisms. |
| Rag2 Knockout | Immunodeficient | Lacks T and B cells | Congenic on BALB/cAnNTac. Tumors may grow more quickly in an immunodeficient host. Amenable to adoptive transfer of immune cells from BALB/cAnNTac or other BALB/c lines. |
| Rag2/Il2rg Knockout (BRG) | Immunodeficient | Lacks T, B and NK cells; dysfunctional dendritic cells. | Congenic on BALB/c. Tumors may grow more quickly in an immunodeficient host. Amenable to adoptive transfer of immune cells from BALB/c lines. |
| NFκB-RE-luc | Reporter | Lacks T and B cells | Potentially useful in imaging host immune responses to syngeneic tumors in vivo. |
Note: Syngeneic tumor take rate and growth kinetics may vary between wild type and immunodeficient mice on the same strain background. A pilot study is always good practice to assess cell line choice and experimental conditions prior to a full study.
| HLA CLASS I | ||
|---|---|---|
Model | Strain Background | Description |
| HLA-A2.1 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-A2.1 class I molecule (representing the HLA-A2 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA-A11 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-A11 class I molecule (representing the HLA-A3 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA-A1 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-A1 class I molecule (representing the HLA-A1 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA-A24 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-A24 class I molecule (representing the HLA-A24 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA-B7 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-B7 class I molecule (representing the HLA-B7 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA-B44 | C57BL/6 or CB6F1 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-B44 class I molecule (representing the HLA-B44 supertype) on the surface of T and B cells. |
| HLA CLASS II | ||
| Abb Knockout/ Transgenic HLA-DR4 | C57BL/6 | Expresses the chimeric HLA-DR4 class II molecule on the surface of T and B cells. |
Are you ready to start your Syngeneic Study?

Syngeneic Cells Lines Derived From Cancer GEMs
Syngeneic tumor cell lines are most commonly derived from wild type inbred strains, but cancer GEM models can also be used. Cancer GEMs are models in which particular mutations have been introduced to provoke spontaneous tumor development. These models are often designed such that they carry mutations found in particular human cancer types. Taconic offers several spontaneous tumor models.
Comparing Syngeneic Tumor Models and Humanized Immune System Mice
When it comes to immuno-oncology, the two most common preclinical systems are syngeneic tumor models and humanized immune system mice implanted with a human cell line or patient-derived xenograft. Learn more about the pros and cons of each approach:
Syngeneic Models Versus Humanized Immune System (HIS) Mice
Syngeneic

- Fully-intact immune system
- Tumor genetically matched with immune system and stroma
- Mouse vs. human differences
Humanized

- Fully-intact immune system
- Tumor genetically matched with immune system and stroma
- Mouse vs. human differences
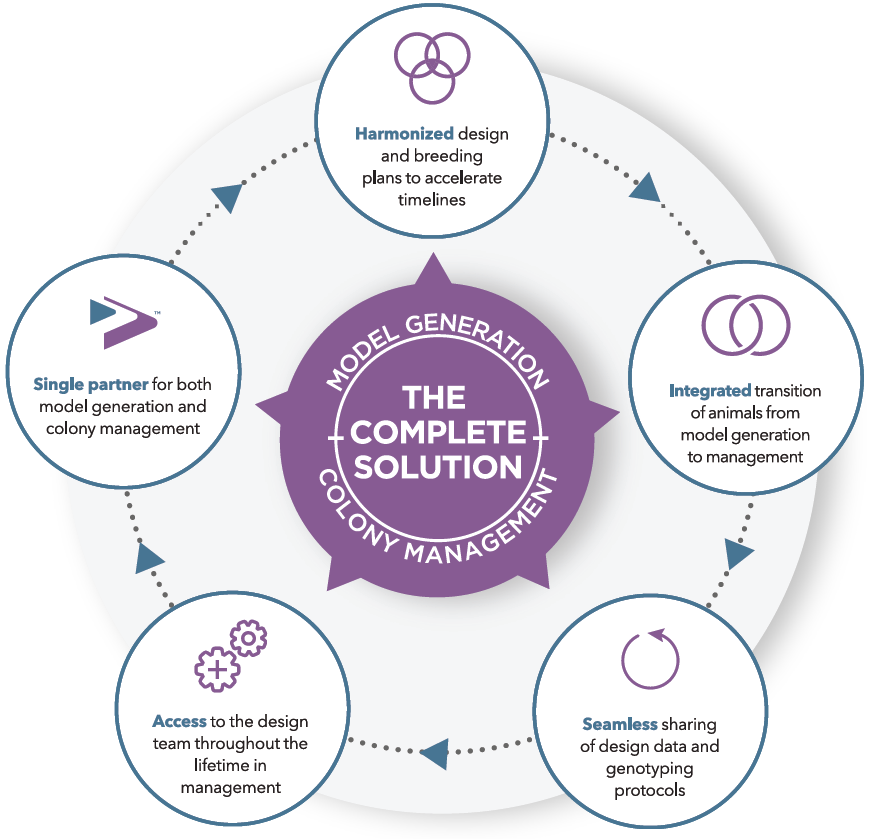
Custom Solutions For Oncology and Immuno-Oncology Research
Taconic Biosciences' globally-recognized scientific project managers support your custom model design project from design to delivery. Each custom model design project develops along an agile framework, letting you reassess and retarget your model fluidly as new data becomes available. You can pause or postpone projects at any time, or even "back up" project milestones via cryopreservation.
Model Generation Solutions
& Breeding Services
- Model Acquisition
- Transition Mutant to Model
- Scaled Breeding
- Specialized Services
- Distribution
Colony Management Solutions
- Extensive Health Standard Options
- True Gnotobiotic Profiles
- Genetic Monitoring Programs
- Scientific Leadership & Success Team
- Custom Solutions for Every Partner
Featured Resources
Get In Touch
Book a complimentary consultation or get support for an existing order
If you need immediate assistance, please contact Customer Service:
Taconic Corporate Offices
Email: info@taconic.com
Phone: +1 (518) 697-3900
273 Hover Ave., Germantown, NY 12526
North American Customer Service
Email: info@taconic.com
Phone: +1 (518) 697-3915
Toll-free: +1 (888) 822-6642
Hours: (Monday - Friday): 7 a.m. - 6 p.m. ET
European Customer Service
Email: info@taconic.com
Phone (Europe and Denmark): +45 70 23 04 05
Phone (Germany): +49 214 50 68 023
Hours: (Monday - Friday): 7 a.m. - 5 p.m. CET










.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)





